Power BI chart titles are crucially important for creating clear and impactful visualizations. Titles and annotations in Power BI charts explain the data and make it easier to understand. Mastering these elements will enhance the overall effectiveness of your reports. And you will communicate your insights clearly and persuasively.
Understanding the Role of Chart Titles in Power BI
Chart titles in Power BI provide the initial point of reference for users interpreting your data visualisations. They provide immediate context, helping viewers grasp the purpose and key message of the chart. Confusing Power BI chart titles can lead to users misinterpreting the data.
The Psychology Behind Effective Chart Titles
Effective Power BI chart titles engage the psychology of how users process information. A well-crafted title can make a significant difference in how quickly and accurately your audience understands your data. Clear, relevant titles help people understand the data and find useful information. Research shows that users focus on titles first, making them a crucial element of any Power BI visualisation.
Best Practices for Crafting Power BI Chart Titles
For Power BI chart titles, following best practices can make a world of difference. A well-crafted title should be concise, descriptive, and aligned with the data presented. Here are a few tips:
- Be Specific: Ensure your title clearly shows what the chart is about. Use specific titles, like “Quarterly Sales Performance by Region,” instead of general titles like “Sales Data.”
- Keep it Short: Aim for a title that is brief yet informative. Long titles can overwhelm and confuse users.
- Update Titles as Needed: If the data or context of your chart changes, be sure to update the title to reflect this.
How Annotations Enhance Clarity in Power BI Visualisations
Power BI chart titles give the main idea, but annotations add extra details to make things clearer. Annotations provide guidance, enabling users to interpret data more accurately. They make data easier to grasp by highlighting key points, explaining anomalies, and providing extra details.
Types of Annotations in Power BI
In Power BI, annotations can take various forms. Here are some common types:
- Text Annotations: These are simple text boxes you can place near data points to provide explanations or additional information.
- Callouts: Use callouts to draw attention to specific data points or trends. This is useful in highlighting anomalies or significant changes in the data.
- Dynamic Annotations: These annotations change based on user interactions, such as filtering or drilling down into the data. This adds a layer of interactivity and personalisation to the visualisation.
By using annotations thoughtfully, alongside Power BI chart titles, you can create visualisations that are not only more informative but also more engaging for your audience. For further reading on effective data visualisation techniques, you can read this article 12 Data Visualization Techniques for Professionals | 2024 Guide (visme.co)
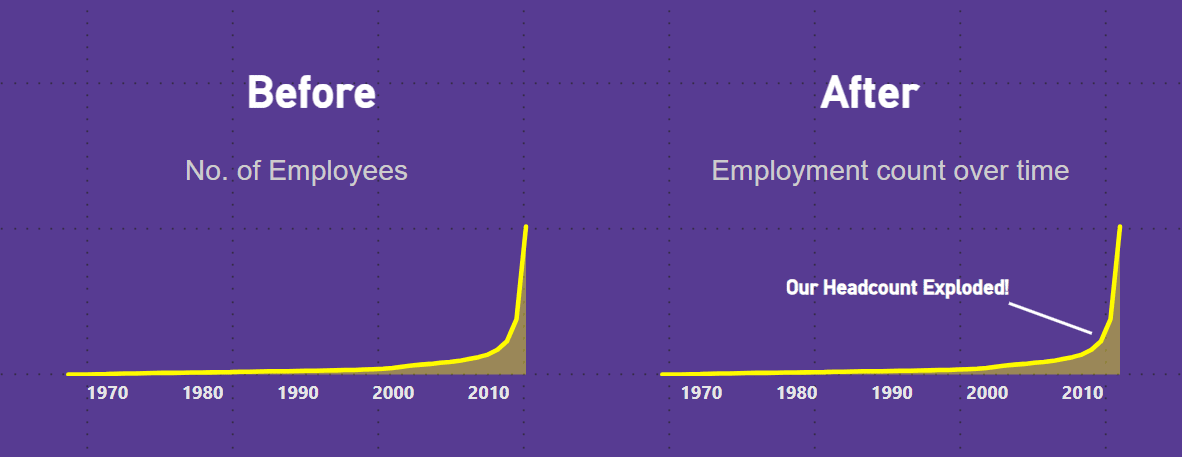
Practical Examples of Effective Annotations in Power BI
Applying Power BI chart titles and annotations effectively requires practice and insight. Let’s explore some practical examples where annotations have significantly improved the clarity and impact of visualisations:
- Example 1: Sales Performance Overview
A simple bar chart showing sales performance across regions can be enhanced with annotations that highlight the top-performing region and provide context, such as recent marketing efforts. By adding a clear Power BI chart title like “Top Regional Sales Performers – Q3 2024,” the visualisation becomes more focused and informative. - Example 2: Year-over-Year Growth Comparison
In a line chart comparing year-over-year growth, annotations can be used to explain dips or spikes in growth, attributing them to specific events (e.g., a product launch or economic downturn). A Power BI chart title like “Year-over-Year Growth with Key Influences Highlighted” sets the stage for the annotations to provide deeper insight. - Example 3: Financial Metrics Dashboard
For a dashboard displaying key financial metrics, annotations can be used to point out trends, such as a steady increase in revenue or a sudden drop in expenses. Using a dynamic title like “Q4 2024 Financial Overview: Trends and Highlights” ensures the Power BI chart titles and annotations work together to tell a comprehensive story.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adding Power BI Chart Titles
Now that we’ve discussed the importance of Power BI chart titles, let’s walk through the process of adding them to your visualisations:
- Select Your Visual: Click on the visualisation in Power BI that you want to add a title to.
- Access the Format Pane: In the visualisation pane, go to the “Format” section.
- Add a Title: Toggle the “Title” option to “On” and enter your desired title in the text box. Make sure to include your focus keyword Power BI chart titles where appropriate.
- Customise the Title: You can customise the font, size, colour, and alignment of the title to fit the style of your report. Ensure the title is visible and aligns with the overall design.
- Update as Necessary: Remember that your Power BI chart titles should evolve with your data. Regularly review and update titles to keep them relevant.
Adding Annotations to Your Power BI Visualisations
Incorporating annotations in your Power BI visualisations can further enhance the clarity provided by Power BI chart titles. Here’s how to add them:
- Choose the Visual: Click on the visual where you want to add an annotation.
- Insert a Text Box: Use the “Text Box” option from the Insert menu to create an annotation. Position the text box near the data point or area you want to highlight.
- Customise the Annotation: Enter your annotation text, and format it using the options available in the Format Pane. Make sure the text is concise and directly related to the data point it refers to.
- Add Dynamic Elements: For more advanced annotations, you can use DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) to create dynamic text that changes based on the data or user interactions.
- Review and Refine: After adding annotations, step back and ensure they complement your Power BI chart titles, providing additional context without overcrowding the visualisation.
By following these steps, your annotations and Power BI chart titles will work together to create a clearer, more engaging narrative in your reports. For additional guidance, you can explore the official Power BI documentation.
Enhancing User Experience with Thoughtful Power BI Chart Titles and Annotations
Incorporating well-crafted Power BI chart titles and annotations is essential for enhancing the overall user experience. These elements work together to guide users through the data, ensuring that insights are not only accessible but also engaging.
The Impact of Contextual Information
Clear Power BI chart titles and relevant annotations provide the necessary context for users to interpret data accurately. For instance, a title like “Monthly Revenue Growth with Market Anomalies Highlighted” immediately informs the user about the chart’s focus, while annotations can pinpoint specific data points where unusual activity occurred.
Without these guiding elements, users might misinterpret the data, potentially drawing incorrect conclusions. By adding both Power BI chart titles and annotations, you ensure that your visualisation tells a complete and accurate story.
Making Data Stories More Engaging
The goal of any visualisation is to make data more accessible and interesting to the audience. Thoughtful Power BI chart titles and annotations can transform a bland chart into a compelling data story. For example, using an engaging title like “Unlocking Revenue Trends: A Deep Dive into Monthly Data” alongside dynamic annotations that highlight significant trends or outliers can draw the viewer in, encouraging them to explore the data further.
To learn more about creating engaging data stories, check out this resource on Storytelling with Data.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Power BI Chart Titles and Annotations
While Power BI chart titles and annotations are powerful tools, they can also be sources of confusion if not used correctly. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Overcomplicating Titles or Making Them Too Vague
A common error is making Power BI chart titles either too complicated or too vague. Overly complex titles can confuse users, while vague titles fail to provide sufficient context. For example, a title like “Financial Overview” is too broad and doesn’t guide the user on what specific aspect of the financials they should focus on. A better approach would be “Q4 2024 Revenue and Expense Analysis.”
The Risk of Overloading Visualisations with Annotations
While annotations are useful, too many can clutter your visualisation, making it difficult to read. This is especially true if the annotations obscure important data points. The key is to strike a balance—use annotations sparingly and only when they add clear value. Every annotation should complement the Power BI chart titles, providing additional clarity without overwhelming the user.
For tips on avoiding these and other mistakes, refer to this helpful guide from Power BI’s best practices.
Advanced Techniques for Customising Power BI Chart Titles and Annotations
Once you’ve mastered the basics of Power BI chart titles and annotations, you can explore more advanced techniques to make your visualisations even more dynamic and personalised.
Using Dynamic Titles Based on Filters and Slicers
One advanced technique is to create dynamic Power BI chart titles that change based on user interactions, such as filters or slicers. For example, if a user selects a specific region in a slicer, the chart title can update to reflect this, e.g., “Sales Performance in North America.”
This approach makes your visualisation more interactive and ensures that the title always accurately describes the data being displayed. To implement dynamic titles, you can use DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) to create formulas that update the title based on selected filters.
Leveraging DAX for Custom Titles and Annotations
DAX can also be used to create custom Power BI chart titles and annotations that go beyond the basic capabilities of Power BI. For example, you can create a title that automatically includes the current date range or the top-performing category in your data. Similarly, you can create annotations that change dynamically based on the data, providing real-time insights that are always relevant.
For those interested in learning more about DAX, the official DAX documentation is an excellent resource.
Tools and Resources for Improving Power BI Chart Titles and Annotations
There are numerous tools and resources available to help you enhance your Power BI chart titles and annotations, making your reports more effective and engaging.
Power BI’s Built-in Features for Titles and Annotations
Power BI offers a range of built-in features that allow you to customise Power BI chart titles and annotations. From basic text boxes and callouts to more advanced dynamic titles using DAX, these tools are essential for creating clear and impactful visualisations.
Additionally, the Format Pane in Power BI provides various options for customising the appearance of your titles and annotations, ensuring they align with your report’s overall design.
External Tools and Plugins
For those looking to take their visualisations to the next level, there are several external tools and plugins available that can enhance the functionality of Power BI chart titles and annotations. Tools like Charticulator and Synoptic Designer offer additional customisation options, allowing you to create highly tailored visualisations that meet specific business needs.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of crafting effective Power BI chart titles and annotations is key to creating visualisations that are not only informative but also engaging and user-friendly. By following the best practices outlined in this article, you can ensure that your Power BI reports effectively communicate the insights your audience needs.
Remember, the process doesn’t end with creating titles and annotations—regular review and refinement are crucial to maintaining the relevance and accuracy of your reports. Whether you’re optimising for SEO, collaborating across teams, or leveraging advanced techniques, the effort you put into these elements will pay off in the clarity and impact of your data stories.
If you have any questions or need further assistance with your Power BI projects, don’t hesitate to contact me. I’m here to help you unlock the full potential of your data visualisations.
FAQs
How do I decide between a descriptive and a creative title?
Decide based on your audience and the purpose of the report. Descriptive titles are usually better for clear communication, while creative titles can be more engaging if the context allows.
Can I automate the addition of annotations in Power BI?
Yes, using DAX and other Power BI features, you can create dynamic annotations that update automatically based on changes in the data.
How do I ensure my titles are SEO-friendly?
Include relevant keywords, keep titles concise, and ensure they accurately reflect the content of the visualisation. This helps improve searchability and user understanding.
What are the best practices for updating annotations?
Regularly review annotations to ensure they remain relevant and accurate as the data evolves. Make updates as necessary to reflect any new insights or changes in the data.
How can I test the effectiveness of my chart titles?
Conduct user testing by gathering feedback from your target audience. This can help you identify any areas where titles might be unclear or confusing, allowing you to make improvements.
